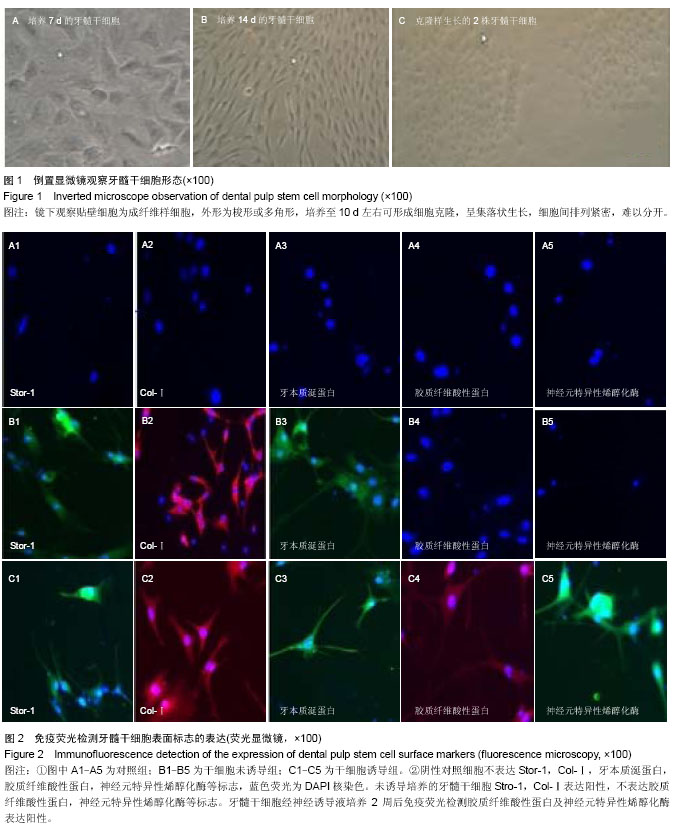
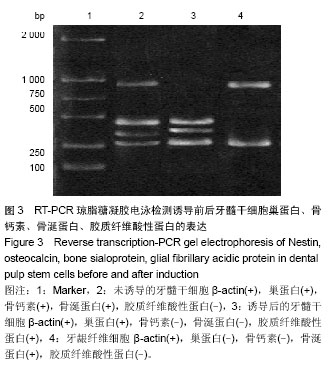
| [1] Zuba-Surma EK, Kucia M, Ratajczak J,et al. "Small stem cells" in adult tissues: very small embryonic-like stem cells stand up.Cytometry A. 2009;75(1):4-13.
[2] Pereira Lda V.The importance of the use of stem cells for public health. Cien Saude Colet. 2008;13(1):7-14.
[3] Cuenca-López MD, Zamora-Navas P, García-Herrera JM,et al. Adult stem cells applied to tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2008;54(1):40-51.
[4] Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J,et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97(25):13625-13630.
[5] Miura M, Gronthos S, Zhao M,et al.SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(10):5807-5812.
[6] Morsczeck C, Schmalz G, Reichert TE,et al. Somatic stem cells for regenerative dentistry.Clin Oral Investig. 2008;12(2):113-118.
[7] Iohara K, Zheng L, Ito M,et al.Side population cells isolated from porcine dental pulp tissue with self-renewal and multipotency for dentinogenesis, chondrogenesis, adipogenesis, and neurogenesis. Stem Cells. 2006;24(11):2493-2503.
[8] Nosrat IV, Smith CA, Mullally P,et al. Dental pulp cells provide neurotrophic support for dopaminergic neurons and differentiate into neurons in vitro; implications for tissue engineering and repair in the nervous system.Eur J Neurosci. 2004;19(9):2388-2398.
[9] Pimentel-Coelho PM, Mendez-Otero R.Cell therapy for neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy.Stem Cells Dev. 2010;19(3):299-310.
[10] Selway LD.State of the science: hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy and hypothermic intervention for neonates. Adv Neonatal Care. 2010;10(2):60-66.
[11] Tsuchiya S, Honda MJ, Shinohara Y,et al.Collagen type I matrix affects molecular and cellular behavior of purified porcine dental follicle cells.Cell Tissue Res. 2008;331(2):447-459.
[12] Yao S, Pan F, Prpic V,et al. Differentiation of stem cells in the dental follicle.J Dent Res. 2008;87(8):767-771.
[13] Perry BC, Zhou D, Wu X,et al. Collection, cryopreservation, and characterization of human dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cells for banking and clinical use.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2008;14(2):149-156.
[14] Woods EJ, Perry BC, Hockema JJ,et al.Optimized cryopreservation method for human dental pulp-derived stem cells and their tissues of origin for bankin g and clinical use. Cryobiology. 2009;59(2):150-157. |